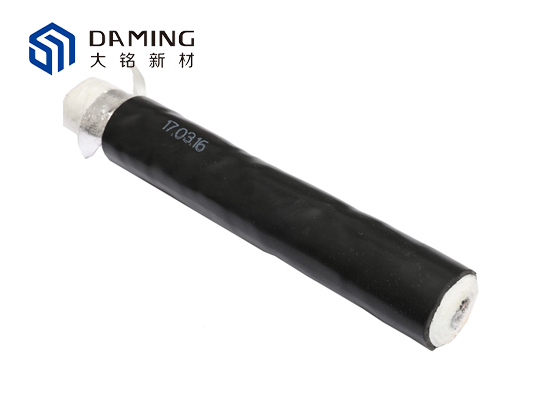
220V Alternating Current Heat Tracing Cable Sampling Tube
1. Introduction to Corrosion-resistant Heated Sampling Composite Pipe:
Corrosion-resistant sampling composite pipe with heat tracing is a vital component in environmental monitoring system. It consists of a group of corrosion-resistant and high-performance resin conduits, supplemented by self-limiting heat tracing (constant power tracing) and compensation cables, plus insulation layer and flame-retardant polyethylene (PE) protective jacket. The self-temperature-limiting tracing belt has the function of automatic temperature limitation, which can ensure the constant temperature in the sampling tube, so as to keep the collected samples consistent with the initial values as much as possible, thus ensuring that the environmental monitoring system can continuously and accurately collect gas samples. According to the actual situation of gas sample composition and temperature, the conduit of corrosion-resistant and heat-tracing sampling composite pipe can be made of different materials, such as PFA, FEP, PVDF, PE and nylon 610. The medium, low and high temperature heat tracing belts can be selected, and compensation wires and power cords can be added according to users' needs. This product was listed as a national key new product promotion plan in 2002, and applied for a national patent in 2001. Our company is currently one of the professional manufacturers of such sampling tubes.
The corrosion-resistant heated sampling composite pipe is a complex system composed of multiple devices, combining multiple systems within a limited cross-section.
-
Sampling System: It can combine various types and materials of sampling pipes, such as PFA, FEP, nylon 610, copper pipes, 316SS, 304SS, etc.
-
Heating System: It includes efficient insulation, flame retardant, and lightweight insulation layers. It utilizes self-limiting temperature heating cables or constant power heating cables.
-
Electrical System: It can be equipped with instrument signal cables, compensation cables, and control cables to meet the needs of instrument display and monitoring.
-
Safety System: The heated sampling composite pipe is a multi-functional pipeline system that can adapt to various process conditions and provide multiple protection measures. It uses aluminum foil or metal wire mesh for shielding and isolation to achieve fire resistance, anti-static, and electromagnetic shielding effects. Additionally, some pipes can be equipped with waterproof membranes and sheaths to enhance flame resistance and UV protection, further enhancing the pipeline's protective performance.
This composite pipeline system has multiple functions and can simplify complex engineering processes. It provides reliable support for remote work and remote system diagnostics. The heating system ensures that the gas inside the pipeline does not condense below the dew point, guaranteeing high-precision measurement results and providing convenient conditions for centralized control and computerized management. Moreover, the reinforced outer sheath effectively prevents cross-contamination and damage caused by other factors.

2. Corrosion-resistant heated sampling composite tube: Basic structure, classification, and model
2.1 Basic structure
1- Outer protective sheath
2- Insulation layer
3- Sampling tube D1
4- Power cord
5- Heating cable
6- Sampling tube D2
7- Core
8- Shielding reflective film
9- Compensation cable
2.2 Classification
2.2.1 Based on the type of heating cable:
a) Self-regulating heating composite tube;
b) Constant power heating composite tube.
2.2.2 Based on different sampling tube materials:
a) Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composite tube;
b) Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) composite tube;
c) Soluble polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) composite tube;
d) Polytetrafluoroethylene (ivory PTFE) composite tube;
e) Stainless steel (0Cr17Ni12Mo2) composite tube.
2.3 Model
2.3.1 The model coding of composite tube products should include at least the following information:
a) Nominal outer diameter, in millimeters (mm);
b) Sampling tube outer diameter, in millimeters (mm);
c) Number of sampling tubes;
d) Sampling tube material;
e) Operating temperature (℃);
f) Type of heating cable, including self-regulating heating and constant power heating.
3. Composite Tube Model Representation:
Introduction to Typical Models
Example 1: Model FHG36-8-b-120-Z represents a nominal outer diameter of 36 millimeters, a sampling tube outer diameter of 8 millimeters, a quantity of 1, a material of fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), a working temperature of 120℃ inside the sampling tube, and a self-regulating heating composite cable.
Example 2: Model FHG42-10(2)-c-180-H represents a nominal outer diameter of 42 millimeters, a sampling tube outer diameter of 10 millimeters, a quantity of 2, a material of soluble polytetrafluoroethylene (PFA), a working temperature of 180℃ inside the sampling tube, and a constant power heating composite cable.
Example 3: Model FHG42-8-6(2)-c-200-H represents a nominal outer diameter of 42 millimeters, a sampling tube outer diameter of 8 millimeters for d1, a quantity of 6 millimeters for d2, a material of soluble polytetrafluoroethylene (PFA), a working temperature of 200℃ inside the sampling tube, and a constant power heating composite cable.
Example 4: Model FHG45-8(2)-6(2)-f-250-H represents a nominal outer diameter of 45 millimeters, a sampling tube outer diameter of 8 millimeters for d1 with a quantity of 2, a sampling tube outer diameter of 6 millimeters for d2 with a quantity of 2, a material of stainless steel (0Cr17Ni12Mo2), a working temperature of 250℃ inside the sampling tube, and with heating.
Heat Tracing Cable Sampling Tube